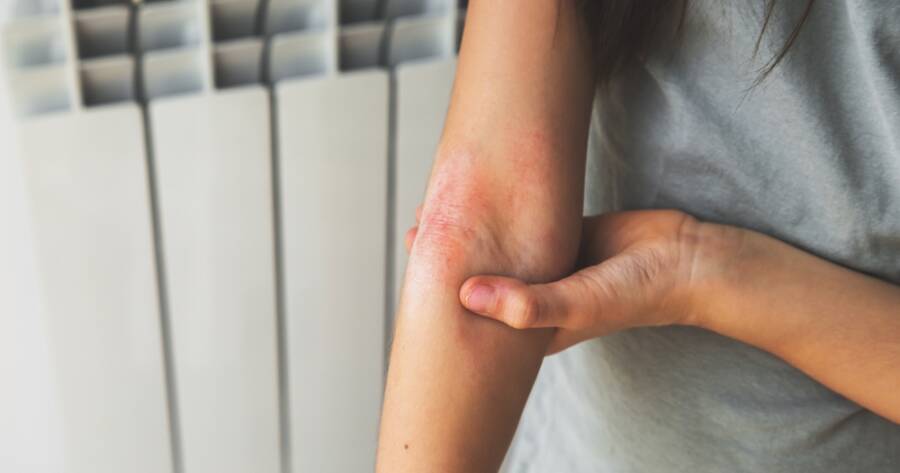
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people globally, including children and adults. It is characterized by persistent itching, redness, dryness, and inflammation, which can severely impact both physical comfort and emotional well-being. This condition often occurs in cycles of flare-ups and remissions, making it challenging to manage. Understanding its underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and exploring effective treatments are essential steps toward better control and improved quality of life.
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often develops in early childhood but can persist or recur throughout adulthood. It is part of the “atopic triad,” which includes asthma and hay fever. Individuals with atopic dermatitis are more likely to have a family history of these conditions, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
This condition occurs in cycles, with periods of flare-ups followed by remissions. While it is not contagious, its visible symptoms can cause emotional distress and social challenges.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis remains unclear, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever increases the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis. Genetic mutations, such as those affecting the filaggrin protein, impair the skin barrier and make it more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An overactive immune system can lead to inflammation and hypersensitivity to environmental triggers.
- Environmental Factors: Common triggers include allergens (pollen, dust mites), irritants (soaps, detergents), extreme weather conditions, and stress.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: A weakened skin barrier allows moisture to escape and irritants to enter, leading to dry and inflamed skin.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary depending on age and severity but commonly include:
- Dry Skin: The skin often feels rough and dehydrated.
- Itching: Persistent itching, which can worsen at night, is a hallmark symptom.
- Redness and Swelling: Inflamed patches of skin, often accompanied by swelling.
- Rashes: Rashes can appear on the face, neck, elbows, knees, hands, and feet.
- Thickened Skin: Chronic scratching may cause lichenification, where the skin becomes thick and leathery.
- Oozing or Crusting: In severe cases, the skin may ooze fluid or form crusts, increasing the risk of infection.
Effective Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Managing atopic dermatitis requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and skincare practices. Here are some effective approaches:
- Moisturizers: Daily use of emollients helps restore the skin barrier and reduce dryness. Look for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic options.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation during flare-ups. Use them as directed to avoid side effects.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal creams, such as tacrolimus, are effective for sensitive areas like the face and neck.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can relieve severe itching, particularly at night.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to controlled ultraviolet (UV) light can reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
- Biologic Therapies: For severe cases, medications like dupilumab target specific immune pathways to control symptoms.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain fabrics, foods, or stress can help prevent flare-ups.
- Proper Skincare Routine: Using gentle cleansers, avoiding hot showers, and applying moisturizer immediately after bathing are essential for managing symptoms.
Living with Atopic Dermatitis
Living with atopic dermatitis requires a proactive approach. Support groups, counseling, and education can help individuals cope with the emotional and social challenges of the condition. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist ensure that treatment plans are adjusted as needed.
Taking Control of Atopic Dermatitis
While atopic dermatitis can be challenging, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments empowers individuals to manage the condition effectively. With the right combination of medical care and self-care, it’s possible to reduce flare-ups, improve skin health, and lead a more comfortable life.