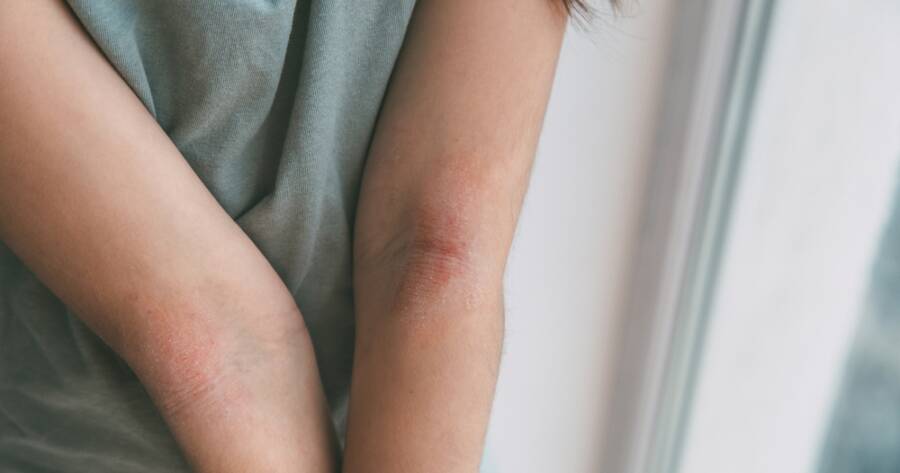
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes itchy, red, dry, and inflamed skin, often leading to discomfort and irritation. While there is no cure, understanding the symptoms, triggers, and prevention strategies can help manage the condition and reduce its impact on daily life.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis symptoms can vary from person to person, but the most common signs include:
- Intense itching: The hallmark symptom, often leading to scratching that worsens the condition.
- Dry and scaly skin: Affected areas may become rough, cracked, or flaky.
- Red or inflamed patches: Typically seen on the face, neck, hands, elbows, and knees, though it can appear anywhere on the body.
- Blisters or oozing lesions: In severe cases, the skin may develop open sores that weep or crust over.
- Thickened skin: Over time, chronic scratching can cause the skin to become thick, leathery, and discolored.
- Increased sensitivity: The skin may react more intensely to irritants and allergens.
Flare-ups can range from mild to severe and may persist for weeks or even months if not properly managed.
Common Triggers of Atopic Dermatitis
Identifying and avoiding triggers is key to preventing flare-ups. Some of the most common triggers include:
- Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold can worsen symptoms.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics (like wool and synthetic materials) can cause irritation.
- Weather changes: Cold, dry air or excessive heat and humidity can aggravate symptoms.
- Food allergies: Dairy, nuts, eggs, and gluten are known to trigger eczema in some individuals.
- Stress: Emotional stress and anxiety can weaken the skin barrier and trigger inflammation.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating from exercise or hot weather can worsen itching and irritation.
- Frequent bathing: Long, hot showers can strip the skin of natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
Prevention Tips for Atopic Dermatitis
While atopic dermatitis cannot be completely prevented, the following strategies can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups:
- Moisturize daily: Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic creams or ointments to keep the skin hydrated.
- Use gentle skincare products: Choose mild, soap-free cleansers and avoid products with harsh chemicals or fragrances.
- Take lukewarm showers: Hot water can dry out the skin; instead, opt for shorter, lukewarm showers.
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics: Cotton and other natural fibers are less likely to irritate the skin.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Identify and avoid triggers: Keep a journal to track flare-ups and identify specific environmental or dietary triggers.
- Use a humidifier: Adding moisture to indoor air can prevent the skin from becoming too dry.
- Seek medical advice: If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a dermatologist for prescription treatments, such as corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immunomodulators.
Managing Atopic Dermatitis: A Proactive Approach for Healthier Skin
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic but manageable skin condition that requires a proactive approach to minimize flare-ups and maintain healthy skin. By recognizing symptoms, avoiding triggers, and following a consistent skincare routine, individuals with eczema can reduce discomfort and improve their quality of life. If symptoms become severe, consulting a dermatologist can provide additional treatment options for long-term relief.